Omega-3s & its beneficial effects in sports
Omega-3 fatty acids have been the talk of the town for their wide range of health benefits. Besides supporting heart health and cognitive function, Omega-3s also play a significant role in sports performance. Can omega-3s really enhance athletes physical abilities? Do athletes’ have higher needs?
Let’s get to know omega-3s and dive into the potential benefits of omega-3s in sports performance.

Is eating “fat” considered unhealthy?
Over the past few decades, many believed that a healthier diet is achieved by reducing total fat intake. This causes them to think that fat is the ultimate villain responsible for negative health outcomes.
However, fats are not created equal.
Fats can be broadly categorized into two main types: saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats have been associated with negative health effects, such as increased cholesterol and heart disease. The unsaturated fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6, are essential fatty acids crucial for brain function, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
These “good fats” are crucial for a healthy diet, proving that not all fats are bad.
Knowing the omega-3 family.
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that are essential for overall health. They are also a type of essential fatty acids. This means that they can only be obtained through food or supplements.
There are three primary members of the omega-3 family:
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid): Found in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Human body cannot use ALA directly and must convert it into the other two more bioactive forms, EPA and DHA.
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): Found primarily in fatty fishes such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. EPA and DHA are the most beneficial for sports performance and recovery.
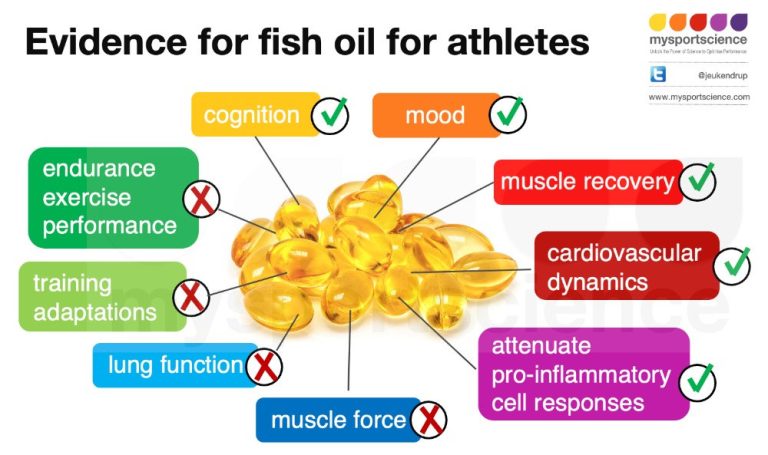
- Reducing Inflammation and Muscle Soreness
Intense exercise, such as strength training, endurance sports, or heavy training loads, often leads to high muscle inflammation and soreness. Omega-3s are known for their anti-inflammatory properties to reduce muscle inflammation after exercise. Lowering inflammation means athletes may experience less soreness, quicker recovery, and a reduced risk of over-training injuries.
2. Enhancing Muscle Protein Synthesis
Muscle growth and repair depend on the process of muscle protein synthesis (MPS), where new proteins are produced to repair damaged muscle fibers. Research shows that omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, can boost MPS, improving muscle recovery after exercise. During periods of immobilization or injury, omega-3s can potentially protect against a reduction in muscle protein synthesis, thus helping to preserve lean muscle mass and function.
Omega-3s support cardiovascular health by improving blood flow, reducing triglyceride levels, and enhancing heart function. For endurance athletes like runners, cyclists, and swimmers, having a strong cardiovascular system is key to optimal performance. Omega-3s can help athletes maintain stamina and increase their ability to perform for extended periods by supporting efficient oxygen delivery to muscles.
4. Boosting Joint Health
Athletes playing high-impact sports like basketball or running often experience joint stress and discomfort. Omega-3s help maintain healthy joints by reducing inflammation and supporting cartilage health. Athletes may find that omega-3s can reduce joint pain and stiffness, allowing them to train better and longer.
How much Omega-3 do athletes need?
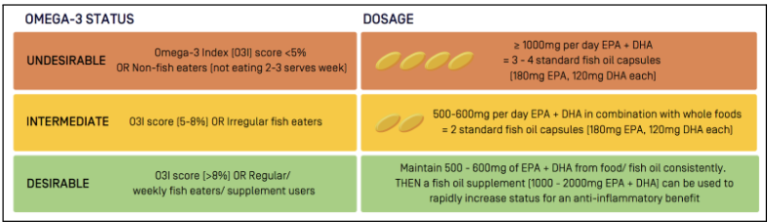
Figure 1: Recommended daily omega-3 dosage
(adopted from AIS Sports Supplement Framework)
Summary
Omega-3s (EPA and DHA) are essential fatty acids that are beneficial for athletes’ well-being and sports performance. These benefits include reducing inflammation, enhancing muscle protein synthesis, improving cardiovascular health, and boosting joint health. The daily requirements of omega-3s can vary based on individual needs and training demands. To meet daily omega-3 needs, athletes should consume enough fatty fishes or consider supplementation under the guidance of health professionals.

